Introduction of Halophyte and Xerophyte
Halophytes are plants which tolerate or even demand sodium chloride concentrations in the soil water they absorb. Depending on the habitat conditions they have developed different strategies to survive in sometimes very high salt content in the soil water. Depending on their tolerance and demands for sodium salts one distinguishes obligate and facultative halophytes. Obligatory means that they need some salt, facultative means they can live also under freshwater conditions.
Xerophyte is a type of plant that is well-adapted to water shortages and exhibits adaptations that enable it to store or conserve water. Xerophytes often live in regions where evapotranspiration (the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration) is greater than precipitation for the region during all or part of the growing season. Adaptations that xerophytes might exhibit include succulent leaves and stems (to store water), fewer stomata (to reduce water loss), and a deep or widespread root system (to optimize water uptake).
This halophyte and xerophytes have special characteristic so that they can survive in this harsh condition.
Apparatus used
Binocular
Bottle
Humidity thermometer
Light intensity meter
Magnifying glass
Measuring tape
Soil thermometer
Hammer probe
Measuring cylinder
Ruler and watch
Morphology characteristic of halophyte
- Have a thick and waxy leaves to reduce transpiration.
- Flexible branches as a protection from strong wind.
- Some have spiny membrane as a protection and to reduce transpiration.
Beach
Our site view
Flora and fauna found
Bintangor sp. (Calophyllum inophyllum)
Chrysanthemum sp.
Eugenia sp.
Fern sp.
Grass
Spider
Soil Characteristic & Microclimates
Time: Morning (9.40am-11.00am)
QUADRAT | DEPTH OF DRY SAND (CM) | TEMPERATURE OF DEPTH 10CM(o C) | AIR TEMPERATURE (o C) | RELATIVE HUMIDITY, RH (%) |
1 | 21 | 28.9 | 28.2 | 85.9 |
2 | 18 | 28.4 | 29.3 | 85.0 |
3 | 24.5 | 27.7 | 28.1 | 88.9 |
4 | 13.5 | 28.5 | 29.4 | 89.4 |
5 | 19 | 28.7 | 28.8 | 92.4 |
Time: Evening (3.35pm-4.10pm)
QUADRAT | DEPTH OF DRY SAND (CM) | TEMPERATURE OF DEPTH 10CM | AIR TEMPERATURE (o C) | RELATIVE HUMIDITY, RH (%) |
1 | - | 31.7 | 29.4 | 77.0 |
2 | - | 32.5 | 30.0 | 79.0 |
3 | - | 30.2 | 30.4 | 78.0 |
4 | - | 31.6 | 30.4 | 80.2 |
5 | - | 29.7 | 29.7 | 80.3 |
Time: Morning (9.40am-11.00am)
BEACH (lux) | WETLAND (lux) | ||
SUNNY | SHADY | SUNNY | SHADY |
63 000 | 6600 | 55 300 | 3900 |
Time: Evening (3.35pm-4.10pm)
BEACH (lux) | WETLAND (lux) | ||
SUNNY | SHADY | SUNNY | SHADY |
110 000 | 8100 | 101 000 | 4800 |
The light intensity of sunlight in beach is higher than wetland. This is because beach is more exposed to the sunlight. Wetland which has covered with higher plant will has lower light intensity. In addition, light intensity of sunlight in evening is higher than morning.
SOIL CHARACTERISTICS: ORGANIC MATERIALS
QUADRAT | BEFORE (ml) | AFTER (ml) | ||||
Sand/soil | Water | Humus | Clay | Organic matter | Sand | |
1 | 38 | 100 | No humus detected | 4.0 | 1.0 | 38 |
2 | 44 | 100 | No humus detected | 0.1 | No organic matter detected | 35 |
3 | 57 | 100 | No humus detected | No clay detected | No organic matter detected | 51 |
4 | 33 | 100 | No humus detected | No clay detected | No organic matter detected | 26 |
5 | 51 | 100 | 5 | No clay detected | 26.0 | 34 |
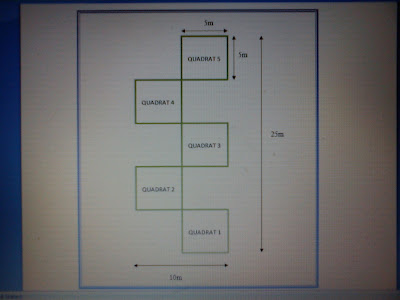
Quadrat 1
Quadrat 2
Quadrat 3
Quadrat 4
Quadrat 5
ECOLOGICAL DETECTIVE
1. Living thing that is growing
a. Plant (example : Eugenia)
2. Something that was once alive
a. Dead leaves
b. Dead branches
3. Something that has undergone change
a. Bitangor – once was stand straight, but now bend toward seashore
4. Something that is impossible to count
a. Sand
b. Insect
c. Plants (example: grasses)
5. Something can not photograph
a. Wind speed
b. Light intensity
c. Temperature
d. Relative humidity (RH)
6. Thing that does not form a necessary part of the ecosystem
a. Garbage
b. Tents
c. Toilet
d. Hall
7. Natural this which could be used as a tool
a. Stone – Hammer, resting place to sit on
b. Wood- Gadget, firewood
c. Dead leaves- to start fire
d. Dead branches- to start fire
8. This that might be food for plants and animals.
a. Soil nutrient-plants
b. Plants-animals
9. Something that won’t be here in 100 years
a. Plants
b. The whole ecology.

























No comments:
Post a Comment